A wrapper around `disclapmix_robust()` that instead of fitting one model for a given number of clusters, fits models until the best model (lowest marginal BIC) is in the interior (with margin `M`) of all number of clusters tried.
disclapmix_adaptive(
x,
label = "DL",
margin = 5L,
criteria = "BIC",
init_y_generator = NULL,
init_v_generator = NULL,
...
)Arguments
- x
Dataset.
- margin
Fit models until there is at least this margin
- criteria
The slot to chose the best model from (BIC/AIC/AICc)
- init_y_generator
Function taking the number of clusters as input and returns `init_y` values
- init_v_generator
Function taking the number of clusters as input and returns `init_v` values
- ...
Passed on to `disclapmix_robust()` (and further to `disclapmix()`)
Value
A list of all `disclapmix` fits
Details
E.g., the best model has 3 clusters and the margin `M = 5`, then this function ensures that models with 1, 2, ..., 3+5 = 8 clusters are fitted. If e.g. then 7 is better than 3, then it continues such that also models with up to 7+5 = 12 clusters are fitted.
Note that models with 1-5 clusters are always fitted.
Examples
data(danes)
db <- as.matrix(danes[rep(1:nrow(danes), danes$n), 1:(ncol(danes)-1)])
fits <- disclapmix_adaptive(db, margin = 5L)
fits
#> [[1]]
#> disclapmixfit from 185 observations on 10 loci with 1 clusters.
#>
#> EM converged: TRUE
#> Number of central haplotype changes: 0
#> Total number of EM iterations: 1
#> Model observations (n*loci*clusters): 1850
#> Model parameters ((clusters*loci)+(loci+clusters-1)+(clusters-1)): 20
#> GLM method: internal_coef
#> Initial central haplotypes supplied: FALSE
#> Method to find initial central haplotypes: pam
#>
#> [[2]]
#> disclapmixfit from 185 observations on 10 loci with 2 clusters.
#>
#> EM converged: TRUE
#> Number of central haplotype changes: 0
#> Total number of EM iterations: 10
#> Model observations (n*loci*clusters): 1850
#> Model parameters ((clusters*loci)+(loci+clusters-1)+(clusters-1)): 32
#> GLM method: internal_coef
#> Initial central haplotypes supplied: FALSE
#> Method to find initial central haplotypes: pam
#>
#> [[3]]
#> disclapmixfit from 185 observations on 10 loci with 3 clusters.
#>
#> EM converged: TRUE
#> Number of central haplotype changes: 0
#> Total number of EM iterations: 10
#> Model observations (n*loci*clusters): 1850
#> Model parameters ((clusters*loci)+(loci+clusters-1)+(clusters-1)): 44
#> GLM method: internal_coef
#> Initial central haplotypes supplied: FALSE
#> Method to find initial central haplotypes: pam
#>
#> [[4]]
#> disclapmixfit from 185 observations on 10 loci with 4 clusters.
#>
#> EM converged: TRUE
#> Number of central haplotype changes: 0
#> Total number of EM iterations: 16
#> Model observations (n*loci*clusters): 1850
#> Model parameters ((clusters*loci)+(loci+clusters-1)+(clusters-1)): 56
#> GLM method: internal_coef
#> Initial central haplotypes supplied: FALSE
#> Method to find initial central haplotypes: pam
#>
#> [[5]]
#> disclapmixfit from 185 observations on 10 loci with 5 clusters.
#>
#> EM converged: TRUE
#> Number of central haplotype changes: 0
#> Total number of EM iterations: 23
#> Model observations (n*loci*clusters): 1850
#> Model parameters ((clusters*loci)+(loci+clusters-1)+(clusters-1)): 68
#> GLM method: internal_coef
#> Initial central haplotypes supplied: FALSE
#> Method to find initial central haplotypes: pam
#>
#> [[6]]
#> disclapmixfit from 185 observations on 10 loci with 6 clusters.
#>
#> EM converged: TRUE
#> Number of central haplotype changes: 0
#> Total number of EM iterations: 31
#> Model observations (n*loci*clusters): 1850
#> Model parameters ((clusters*loci)+(loci+clusters-1)+(clusters-1)): 80
#> GLM method: internal_coef
#> Initial central haplotypes supplied: FALSE
#> Method to find initial central haplotypes: pam
#>
#> [[7]]
#> disclapmixfit from 185 observations on 10 loci with 7 clusters.
#>
#> EM converged: TRUE
#> Number of central haplotype changes: 0
#> Total number of EM iterations: 30
#> Model observations (n*loci*clusters): 1850
#> Model parameters ((clusters*loci)+(loci+clusters-1)+(clusters-1)): 92
#> GLM method: internal_coef
#> Initial central haplotypes supplied: FALSE
#> Method to find initial central haplotypes: pam
#>
#> [[8]]
#> disclapmixfit from 185 observations on 10 loci with 8 clusters.
#>
#> EM converged: TRUE
#> Number of central haplotype changes: 0
#> Total number of EM iterations: 17
#> Model observations (n*loci*clusters): 1850
#> Model parameters ((clusters*loci)+(loci+clusters-1)+(clusters-1)): 104
#> GLM method: internal_coef
#> Initial central haplotypes supplied: FALSE
#> Method to find initial central haplotypes: pam
#>
#> [[9]]
#> disclapmixfit from 185 observations on 10 loci with 9 clusters.
#>
#> EM converged: TRUE
#> Number of central haplotype changes: 0
#> Total number of EM iterations: 29
#> Model observations (n*loci*clusters): 1850
#> Model parameters ((clusters*loci)+(loci+clusters-1)+(clusters-1)): 116
#> GLM method: internal_coef
#> Initial central haplotypes supplied: FALSE
#> Method to find initial central haplotypes: pam
#>
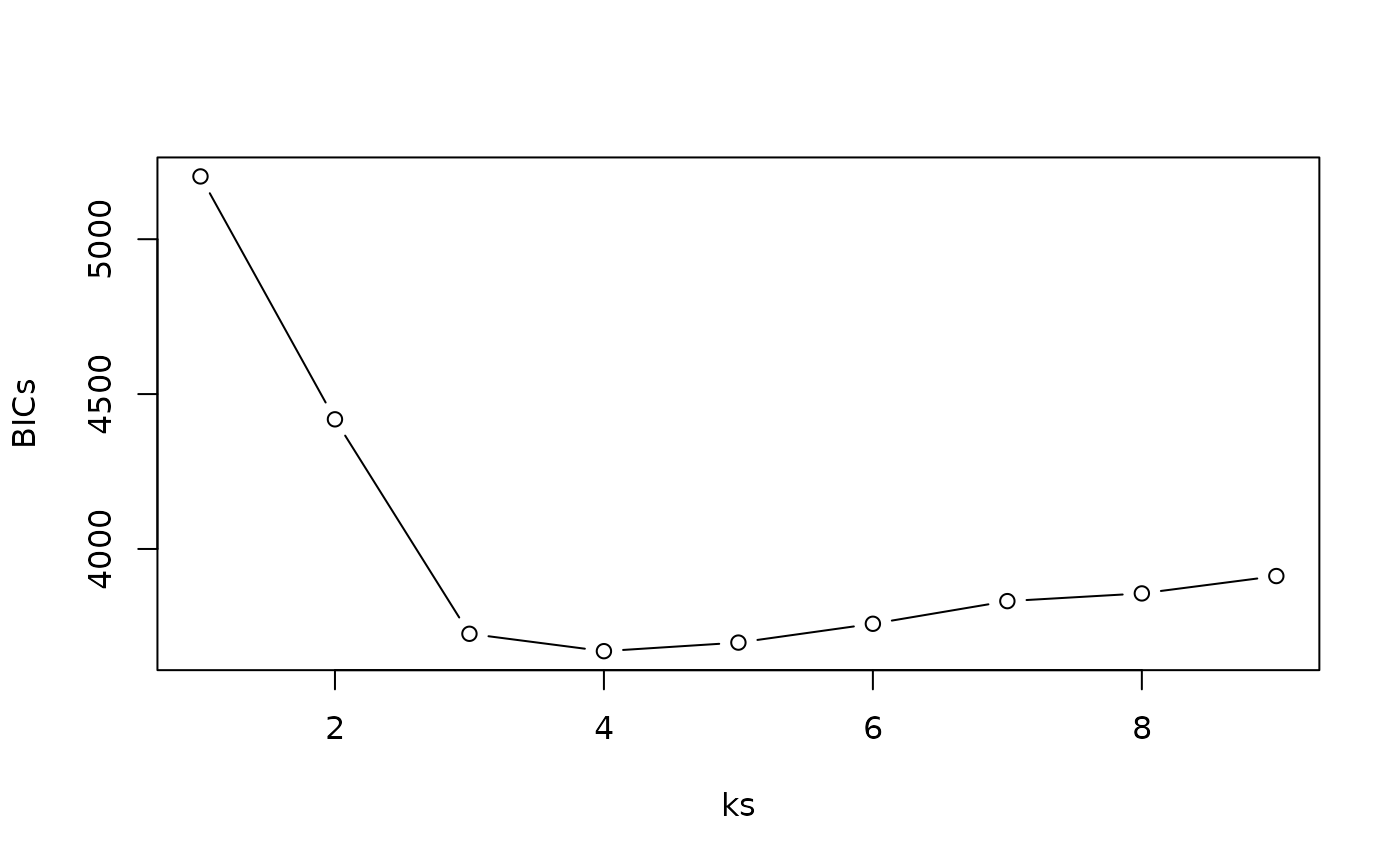
BICs <- sapply(fits, function(x) x$BIC_marginal)
BICs
#> [1] 5202.647 4418.495 3726.156 3670.030 3697.715 3758.452 3831.587 3856.471
#> [9] 3912.551
ks <- sapply(fits, function(x) nrow(x$y)) # Always same as seq_along(fits)
ks
#> [1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
max_k <- max(ks)
best_k <- which.min(BICs)
max_k
#> [1] 9
best_k
#> [1] 4
max_k - best_k # = margin = 5
#> [1] 5
plot(ks, BICs, type = "b")
 fits_clara <- disclapmix_adaptive(db, margin = 5L, init_y_method = "clara")
fits_clara <- disclapmix_adaptive(db, margin = 5L, init_y_method = "clara")